When it comes to keeping your home comfortable and energy-efficient, proper attic insulation plays a critical role. How thick should attic insulation be determined through the right thickness for your attic insulation is not a one-size-fits-all task.
It depends on several factors, such as your climate, the type of insulation you use, and your budget. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the importance of attic insulation, the factors that influence its thickness, and how to determine the ideal thickness for your home.
Understanding Attic Insulation
Attic insulation is like a cozy blanket for your home, regulating temperature and keeping it comfortable. It serves two primary purposes:
- Thermal Barrier
Insulation prevents heat from escaping during the winter and entering during the summer, which significantly reduces your energy bills.
- Moisture Control
It helps prevent moisture from seeping into your attic, which can cause various issues like mold growth and structural damage.
Factors Affecting Attic Insulation Thickness
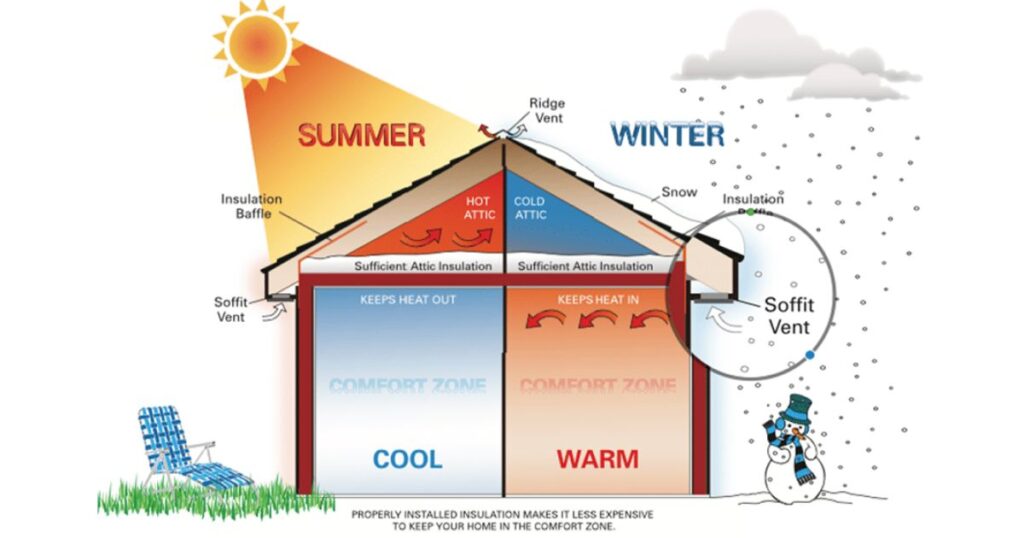
The ideal thickness for attic insulation varies based on several key factors:
- Climate
Your local climate plays a pivotal role in determining the thickness of your attic insulation. Colder climates require thicker insulation to keep your home warm, while in warmer climates, you need less insulation for cooling efficiency.
- Type of Insulation
Various types of insulation materials are available, such as fiberglass, cellulose, and foam boards. Each has different R-values, which measure their thermal resistance. Higher R-values indicate better insulation, and the recommended thickness will vary accordingly.
- Current Insulation
If your home already has insulation, you might not need to replace it entirely. Sometimes, adding more insulation on top of the existing layer can be sufficient to achieve the desired thickness.
- Budget
Your budget also influences your choice of insulation thickness. Thicker insulation is more effective but can be costlier. It’s essential to find a balance between budget and performance.
Signs You Don’t Have Enough Attic Insulation
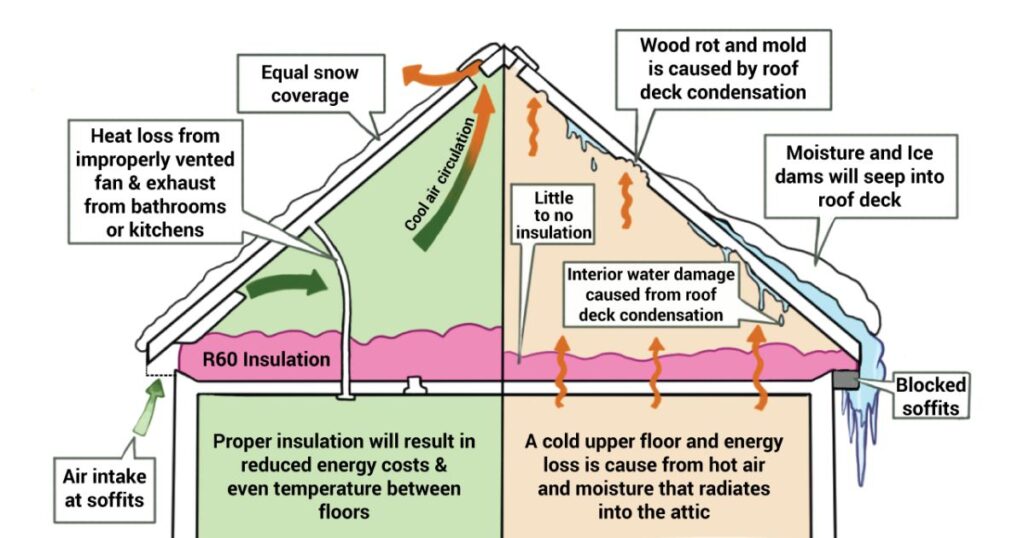
A well-insulated attic is essential for maintaining a comfortable and energy-efficient home. Inadequate attic insulation can lead to various problems, impacting your comfort and energy bills.
To help you identify whether you have enough attic insulation, here are some common signs that suggest your attic may be under-insulated:
Fluctuating Indoor Temperatures
One of the most noticeable signs of insufficient attic insulation is inconsistent indoor temperatures. If you find that your home is too hot in the summer and too cold in the winter, it’s a clear indication that your insulation may not be doing its job effectively.
High Energy Bills
Inadequate attic insulation allows heat to escape during the winter and enter during the summer. This means your heating and cooling systems must work harder to maintain a comfortable temperature, leading to higher energy bills. If you’ve noticed a significant increase in your energy costs, it’s time to inspect your attic insulation.
Uneven Heating or Cooling
Rooms that are far from the HVAC system or located directly below the attic may experience uneven heating or cooling. Inadequate insulation allows conditioned air to dissipate quickly, resulting in temperature disparities throughout your home.
Ice Dams on the Roof
In regions with cold winters, ice dams can form on the roof’s edge when warm air escapes through the attic. This can lead to water damage as the ice dams melt. Proper insulation can prevent this issue.
Excessive Moisture and Mold
Inadequate insulation can allow moisture to accumulate in your attic, leading to mold growth. Mold not only damages your home but also poses health risks to your family. If you notice signs of moisture or mold in your attic, it’s a red flag.
Drafts and Cold Spots
Feeling drafts or encountering cold spots in your home, especially near windows, doors, or walls adjoining the attic, can indicate that your attic insulation is insufficient to prevent air leaks.
Aging or Damaged Insulation
Over time, insulation can degrade, become compressed, or even get damaged by pests. If you have old or visibly deteriorated insulation in your attic, it’s a clear sign that it needs replacement or reinforcement.
Insect or Pest Infestations
Gaps or damaged insulation can provide easy access for insects and pests into your home. If you notice an increase in pest activity, it could be due to insufficient attic insulation.
Unusually High Indoor Humidity
Attics with poor insulation may not adequately vent moisture. This can result in higher indoor humidity levels, which can be uncomfortable and potentially harmful to your home’s structure.
Sound Transmission
If you can hear external noises more clearly than usual or your home doesn’t provide the sound insulation you desire, it may be due to insufficient attic insulation. Proper insulation can help reduce sound transmission.
Assessing what you’ve got
| What you see: | What it probably is | Depth (inches) | Total Insulation R-value |
| Loose fibers | light-weight yellow, pink, or white | fiberglass | =2.5 x depth |
| dense gray or near white may have black specs | rock wool | fiberglass | =2.8 x depth |
| small gray flat pieces or fibers (from newsprint) | cellulose | vermiculite or perlite | =3.7 x depth |
| Granules | light-weight | vermiculite or perlite | =2.7 x depth |
| Batts | light-weight yellow, pink, or white | fiberglass | =3.2 x depth |
Calculating the Ideal Thickness
To determine the ideal thickness of attic insulation for your home, follow these steps:
- Identify Your Location’s Climate Zone
The U.S. is divided into climate zones, each with its recommended R-value for attic insulation. Use the Department of Energy’s recommendations as a reference point.
- Check the Current Insulation
Assess the existing insulation in your attic. Determine its type, R-value, and condition. If it’s in good shape, you might only need to add insulation to reach the desired R-value.
- Calculate the R-Value Required
Based on your climate zone and the type of insulation you’re using, calculate the R-value required to achieve optimal energy efficiency. You can use online calculators or consult with a professional for a precise calculation.
- Purchase the Right Amount
Now that you know the required R-value, purchase the right amount of insulation material to achieve this value. Be sure to choose a high-quality insulation product for the best results.
Conclusion
Proper attic insulation is crucial for maintaining a comfortable and energy-efficient home. The idea of how thick should attic insulation be depends on your location’s climate, the type of insulation, your current insulation, and your budget.
By understanding these factors and following the steps to calculate the required R-value, you can make an informed decision about how thick your attic insulation should be. Investing in the right insulation thickness will not only save you money but also contribute to a more sustainable and comfortable living environment.










